If you have a vineyard, then you need to know some tips n how to make it healthy.
Creating a thriving vineyard requires careful planning, consistent care, and a deep understanding of viticulture practices.
Here are the key steps to help your vineyard thrive.
Site Selection
Consider factors such as climate, soil type, sunlight exposure, and drainage.
Different grape varieties thrive in different conditions, so match the site to the grapes you intend to grow.
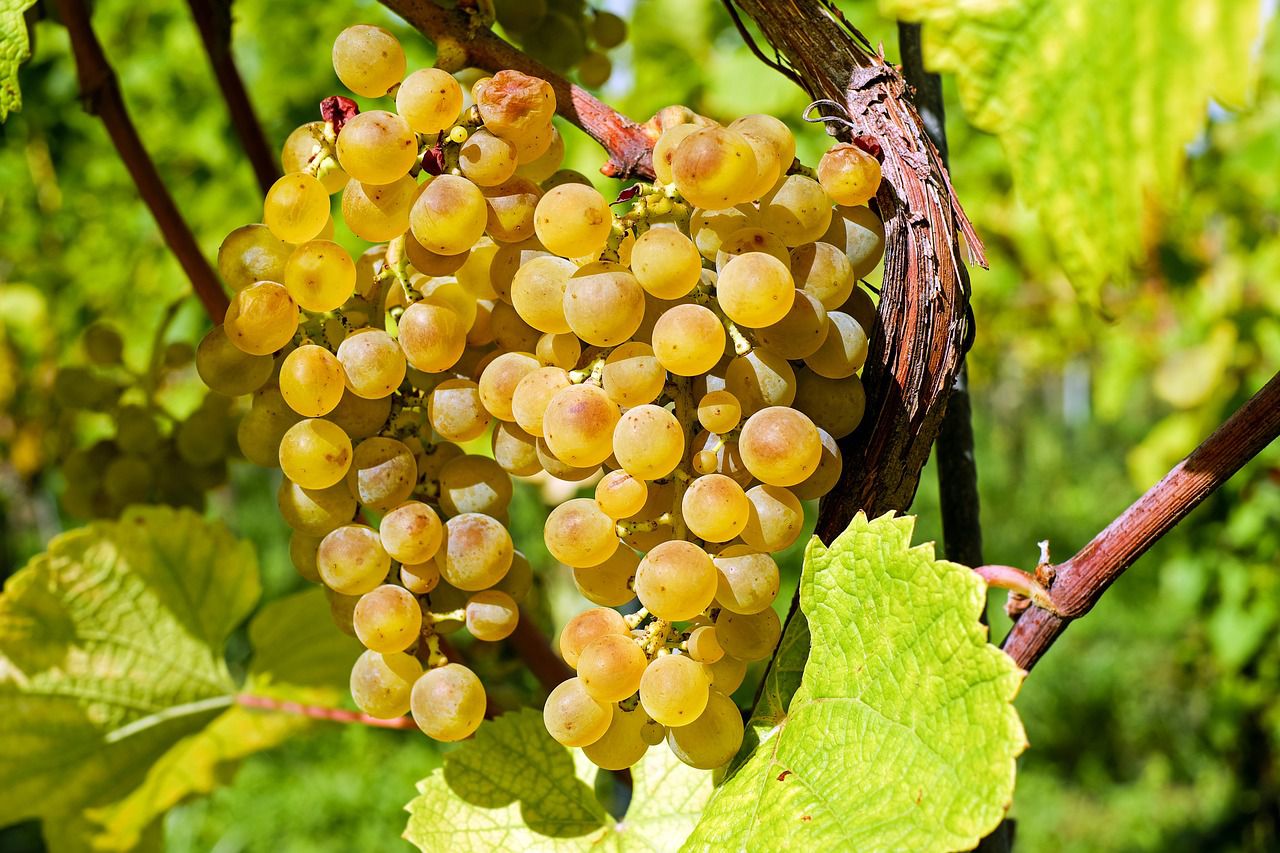

Grape Variety Selection
Choose grape varieties that are well-suited to your climate and soil type.
Different grapes thrive in different conditions, so research and consult local experts to make informed choices.
Planting
Plant grapevines during the appropriate time of the year, usually in the spring or fall.
Follow proper planting techniques, ensuring proper spacing and depth.
Train young vines to grow along a trellis system.
Pruning and Training
Pruning is essential to manage vine growth, encourage proper fruiting, and improve air circulation.
Train the vines along a trellis or support system to optimize sunlight exposure and airflow.
Irrigation
Provide consistent and appropriate irrigation to ensure proper vine hydration.
Balance water availability to prevent over- or under-watering, which can affect grape quality.
Pest and Disease Management
Monitor your vineyard regularly for signs of pests and diseases.
Implement integrated pest management practices, which may include using beneficial insects, traps, and appropriate pesticides only when necessary.
Fertilization
Apply fertilizers based on soil test recommendations and grapevine nutrient requirements.
Avoid excessive fertilization, which can lead to imbalanced growth and poor fruit quality.